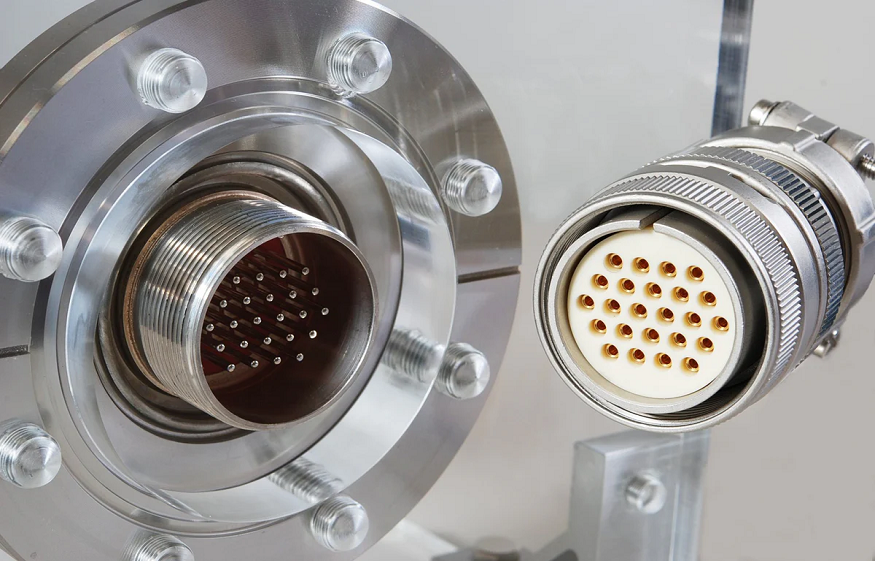
In industrial settings, hermetic feedthroughs play a critical role in maintaining electrical connectivity while preserving airtight or vacuum-sealed environments. These components are essential for high-reliability systems used in aerospace, medical devices, semiconductor manufacturing, vacuum equipment, and harsh industrial environments. Understanding the types of hermetic feedthroughs available helps engineers, designers, and maintenance teams select the right component for their specific applications.
What Are Hermetic Feedthroughs?
A hermetic feedthrough is an electrical or optical interface that allows signals, power, or fluids to pass through a sealed barrier without compromising the integrity of the environment. The seal prevents air, moisture, or contaminants from entering sensitive equipment, which is especially important in high-vacuum systems, cryogenic environments, and high-pressure industrial applications.
Hermetic feedthroughs are typically constructed using a combination of metals, ceramics, and glass, ensuring long-term reliability and stability under extreme conditions.
Glass-to-Metal Hermetic Feedthroughs
Glass-to-metal hermetic feedthrough are among the most commonly used in industrial applications. In this type, metal pins are embedded in a glass insulator, which is then fused to a metal flange or housing. This construction provides excellent vacuum sealing, electrical insulation, and resistance to thermal expansion.
Applications:
- High-voltage electrical systems
- Vacuum chambers and furnaces
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
Glass-to-metal feedthroughs are favored for their high dielectric strength and long-term stability, making them ideal for critical industrial operations.
Ceramic-to-Metal Hermetic Feedthroughs
Ceramic-to-metal feedthroughs use a ceramic insulator, often alumina, fused to a metal housing with metallization techniques. These feedthroughs are extremely durable and can withstand higher temperatures and mechanical stresses than glass-to-metal variants.
Applications:
- Aerospace and defense electronics
- Industrial furnaces
- High-pressure and high-temperature sensors
Their robust construction makes ceramic-to-metal feedthroughs suitable for environments where extreme heat, vibration, or pressure is expected.
Coaxial Hermetic Feedthroughs
Coaxial hermetic feedthroughs are designed for transmitting high-frequency RF signals while maintaining hermetic sealing. These feedthroughs use coaxial connectors with precise impedance control to prevent signal loss and reflections.
Applications:
- RF and microwave systems
- Satellite communication devices
- Industrial radar equipment
Coaxial hermetic feedthroughs are critical in industries that require both signal integrity and environmental protection.
Multi-Pin Hermetic Feedthroughs
Multi-pin hermetic feedthroughs feature multiple electrical paths through a single sealed unit, reducing space requirements while maintaining airtight integrity. Pins are individually insulated and sealed to prevent cross-talk and maintain high reliability.
Applications:
- Medical devices and imaging equipment
- Control systems in industrial automation
- Aerospace instrumentation
These feedthroughs simplify wiring in complex systems while ensuring all connections remain sealed and protected.
High-Voltage Hermetic Feedthroughs
High-voltage hermetic feedthroughs are specifically designed to handle voltages ranging from several hundred volts to tens of kilovolts. These feedthroughs are engineered with additional insulation, spacing, and sealing techniques to prevent arcing, corona discharge, and leakage.
Applications:
- Power generation equipment
- Particle accelerators
- Industrial X-ray and plasma systems
They are essential in industries where high-voltage integrity must be maintained in a sealed environment.
Optical Hermetic Feedthroughs
Optical feedthroughs allow fiber optic signals to pass through a hermetic barrier without compromising vacuum or pressure integrity. These feedthroughs use special glass or ceramic seals to maintain the optical fiber alignment while ensuring environmental protection.
Applications:
- Fiber optic communication in industrial settings
- Medical imaging equipment
- Scientific instrumentation
Optical hermetic feedthroughs are increasingly important as industrial systems rely on high-speed optical signal transmission.
Selecting the Right Hermetic Feedthrough
Choosing the appropriate feedthrough depends on several factors:
- Type of signal: Electrical, RF, high-voltage, or optical
- Operating environment: Vacuum, high pressure, high temperature, or corrosive conditions
- Number of connections: Single-pin, multi-pin, or coaxial
- Mechanical durability: Resistance to vibration, shock, and thermal cycling
Working with a knowledgeable supplier or engineer ensures the selected feedthrough meets the operational and environmental requirements of your industrial system.
Conclusion
Hermetic feedthroughs are indispensable in modern industrial applications, providing reliable electrical or optical connections while protecting sensitive equipment from environmental hazards. Whether it’s glass-to-metal, ceramic-to-metal, coaxial, multi-pin, high-voltage, or optical, each type of feedthrough has unique advantages and specific applications. By understanding the different types, industrial engineers can select the optimal hermetic feedthrough to ensure performance, safety, and longevity in demanding environments.